

BS 7406:1991 is a British Standard that specifies procedures for measuring the water vapour transmission rate (WVTR) of sheet materials. This standard was published on January 31, 1991, and has since been superseded by BS ISO 9932:2021 as of March 3, 2021
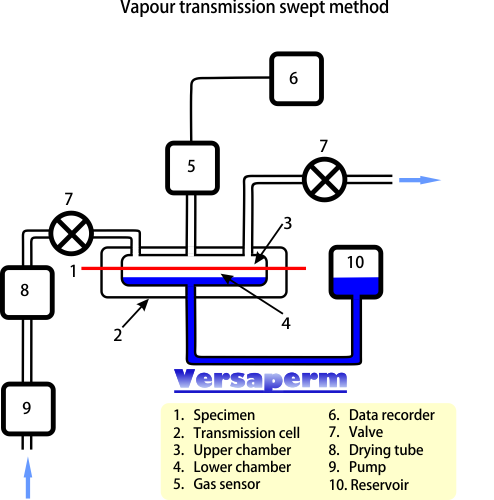 The standard outlines two primary methods for determining WVTR:
The standard outlines two primary methods for determining WVTR:
Method A: Dynamic Sweep Gas Method – This technique involves passing a dry carrier gas over the surface of the test specimen and measuring the amount of water vapour transmitted.
Method B: Static Gas Method – In this method, the test specimen separates two chambers, one with a known humidity and the other dry. The increase in humidity in the dry chamber over time indicates the WVTR.
These methods are applicable to materials up to 38 mm thick and can measure WVTRs ranging from 0.05 g/(m²·d) to 65 g/(m²·d)
BS 7406:1991 includes detailed information on:
Scope and Definitions – Clarifies the applicability and terminology used.
Apparatus and Materials – Describes the equipment and materials required for testing.
Sampling and Test Piece Preparation – Outlines procedures for selecting and preparing specimens.
Testing Procedures – Provides step-by-step instructions for both dynamic and static methods
Expression of Results – Details how to calculate and report WVTR values.
Precision and Test Report – Discusses the accuracy of the methods and the necessary contents of a test report.
Annexes – Includes supplementary information on saturated saline solutions (Annex A), calibration procedures (Annex B), and a comparison between dynamic and gravimetric methods (Annex C).
BS 7406:1991 has been superseded by BS ISO 9932:2021, which aligns with international standards and may include updated methodologies and broader applicability. For applications requiring current compliance, it is advisable to refer to BS ISO 9932:2021